|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||

|
||||||||||||||
|
Double Plasma Device Laboratory & Helicon Laboratory |
||||||||||||||
|
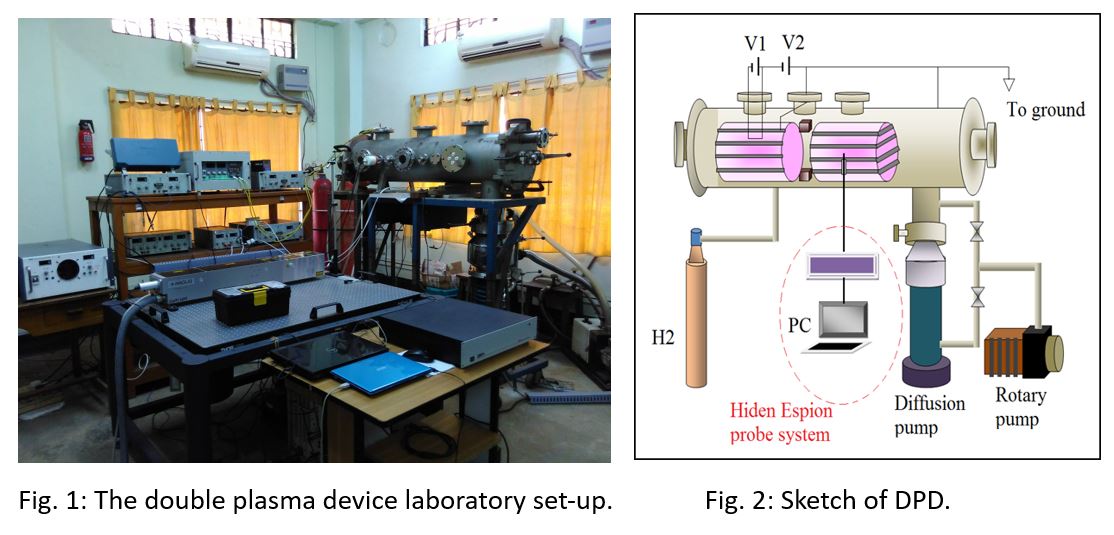
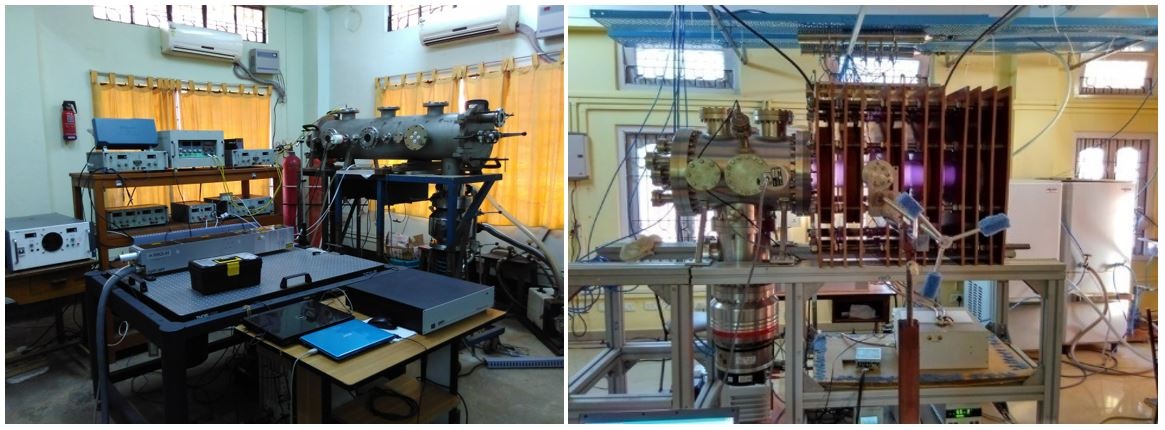
Overview of Double Plasma Device Laboratory and Helicon Plasma Source LaboratoryDouble Plasma Device Laboratory: Brief introduction and activities The double plasma device (DPD) laboratory’s experimental chamber (120 cm long, 30 cm diameter) is the first one bought by the institute in the early nineties (Fig. 1). Initially it was used to produce plasma by the glow discharge process. Since 2003, using two cylindrical magnetic cages (length 32 cm and diameter 25 cm), filament discharge plasmas (in Argon and in Hydrogen gases) have been produced in two regions in this chamber (Fig. 2). Working pressure is usually kept at ~ 10–4 mbars after evacuating the chamber to ~ 10–6 mbars with a rotary and diffusion pump (1000 l/s). Full lined cusped magnetic cages (1.2 kG/4 kG surface field strength) confine these two regions in which plasmas can be produced separately if needed. These regions, usually separated by a grid and also magnetic filter, as experimental aim demands, are called the source and target regions. As plasma can be produced, confined and studied in both these regions therefore it is called a double plasma device. DPDs allow setting up of various experimental configurations with little effort and difficulty. Such experimental systems are capable of performing studies on diffused plasma characteristics, generation of electron and ion beams, launching of waves, sheath characteristics and a host of other plasma phenomena. With minor changes it can be used to conduct studies on negative ion production and its dynamics. Therefore, DPDs are very versatile and attractive to conduct experiments.
Helicon Plasma Source Laboratory: Brief introduction and activities The Helicon Plasma Source (HeliPS) (Figs. 1, 2) designed and developed at the Centre of Plasma Physics-Institute for Plasma Research is a versatile device which operates in magnetic field upto 500 G and can perform a broad range of research activities. The vacuum chamber consists of two parts: source and expansion chambers. The source chamber of borosilicate glass is of 10 cm diameter, 60 cm length and 0.5 cm thickness. The stainless steel expansion chamber is of length 40 cm and diameter 30 cm. A helicon discharge provides clear benefits such as longer operational lifetime, better coupling, stability at low pressures, higher plasma densities (1011 cm-3), low electron temperature (2-10 eV) at comparatively lower radio frequency power and better plasma uniformity over the entire plasma volume. Experiments are performed in gases such as Argon, Oxygen, Hydrogen and Nitrogen with emphasis on producing ion-ion plasmas in electronegative gases with RF power supply of 3 kW and 13.56 MHz. External circuit parameters, such as antenna current, plasma resistance, and internal parameters, such as electron density and temperature, have been measured. Mode transition studies from capacitive to inductive and finally to helicon mode as well as ion-ion plasma studies have also been carried out. Ion – ion plasmas have considerable importance in plasma R & D as it is widely used in the semiconductor industry for etching and deposition of thin films and have applications in negative ion sources and in future advanced thruster development for deep space mission. HeliPS can also be used for experimental studies on basic helicon plasma properties, nonlinear studies, wave propagation, wave coupling, and plasma instability.
Research - IResearch - II
| ||||||||||||||